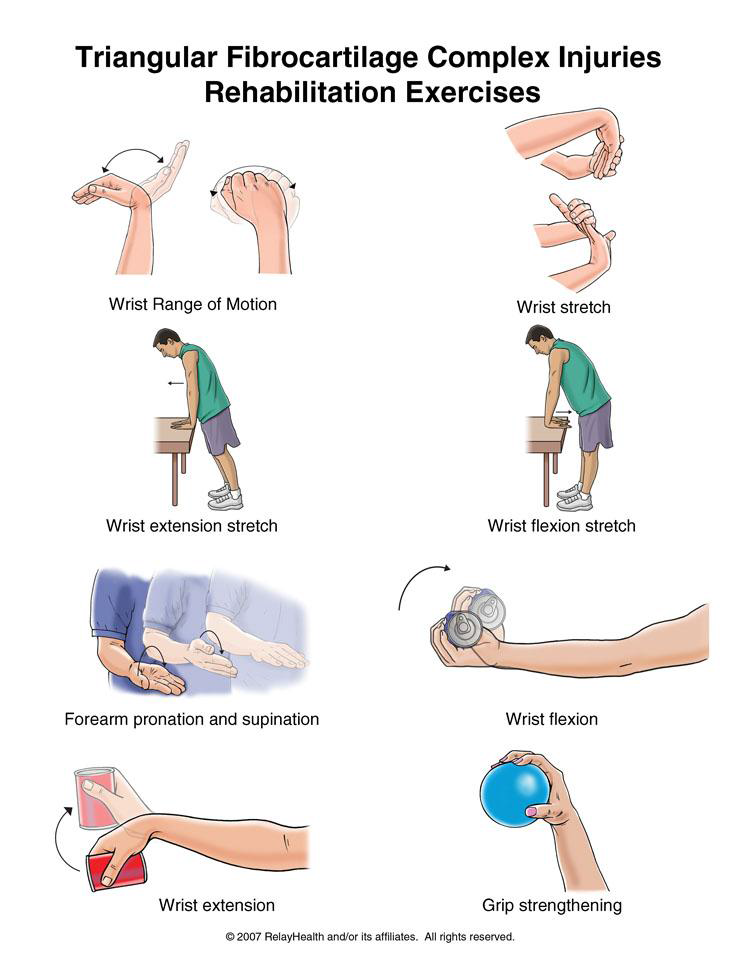
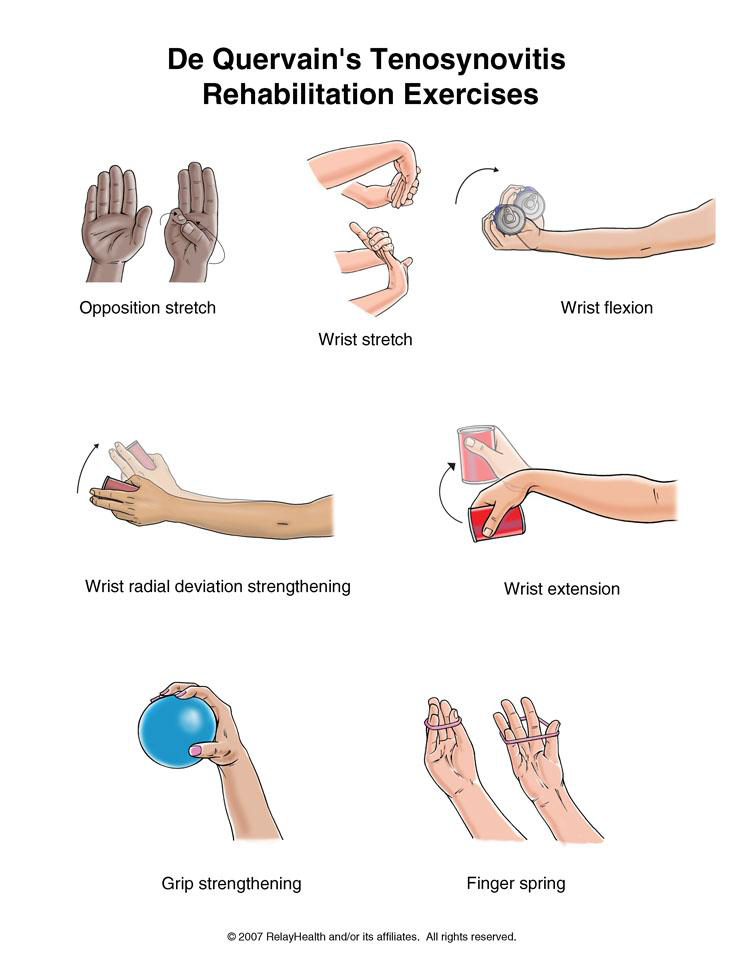
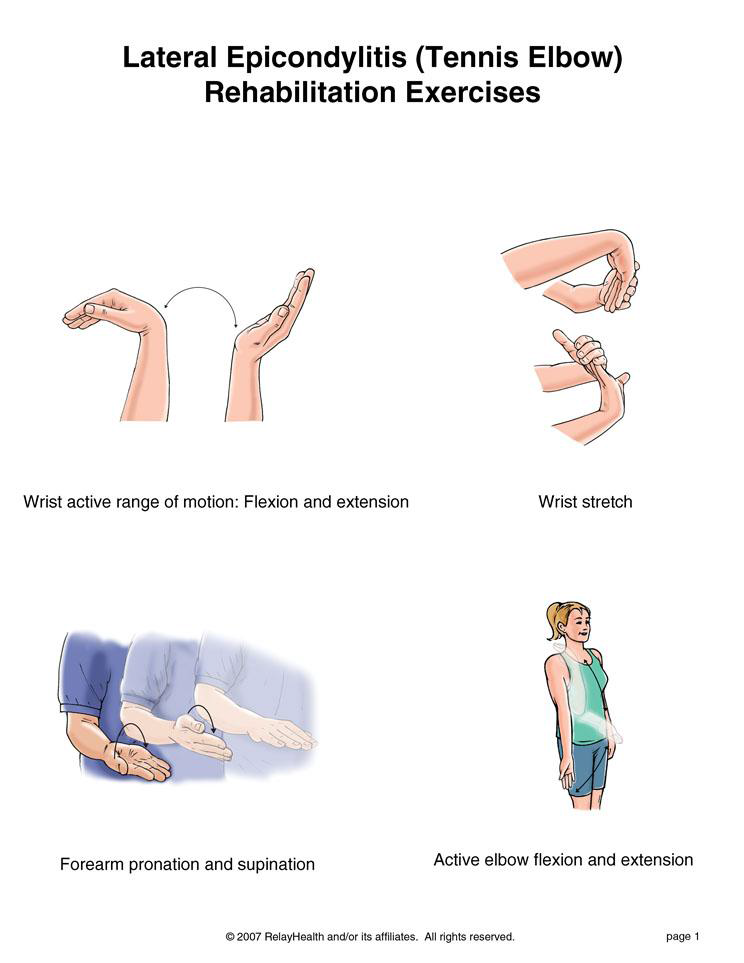
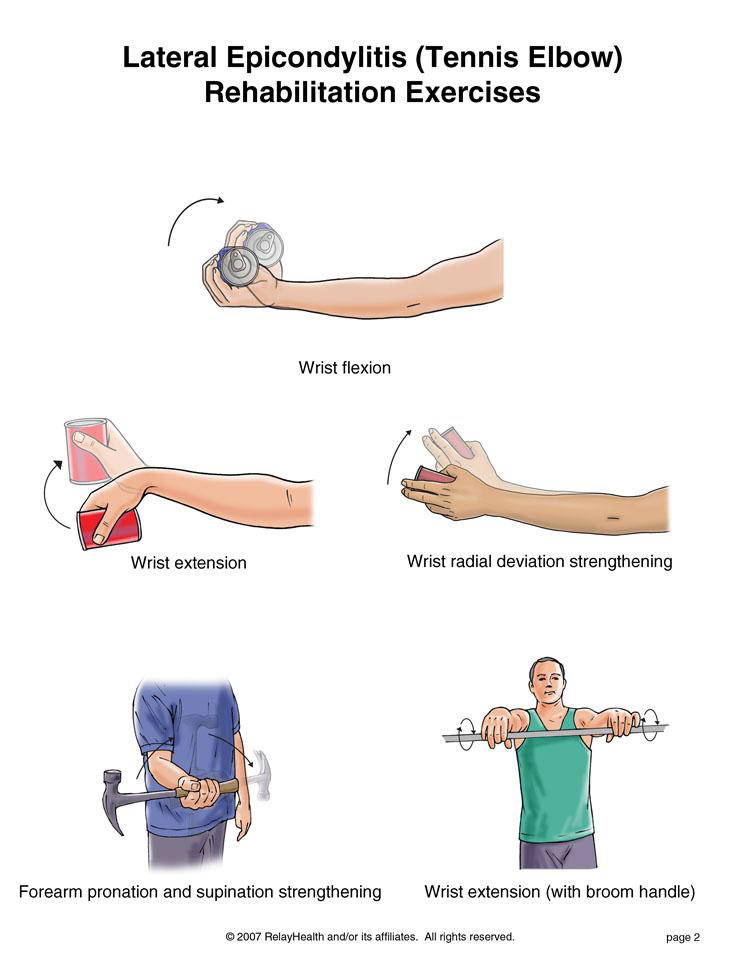
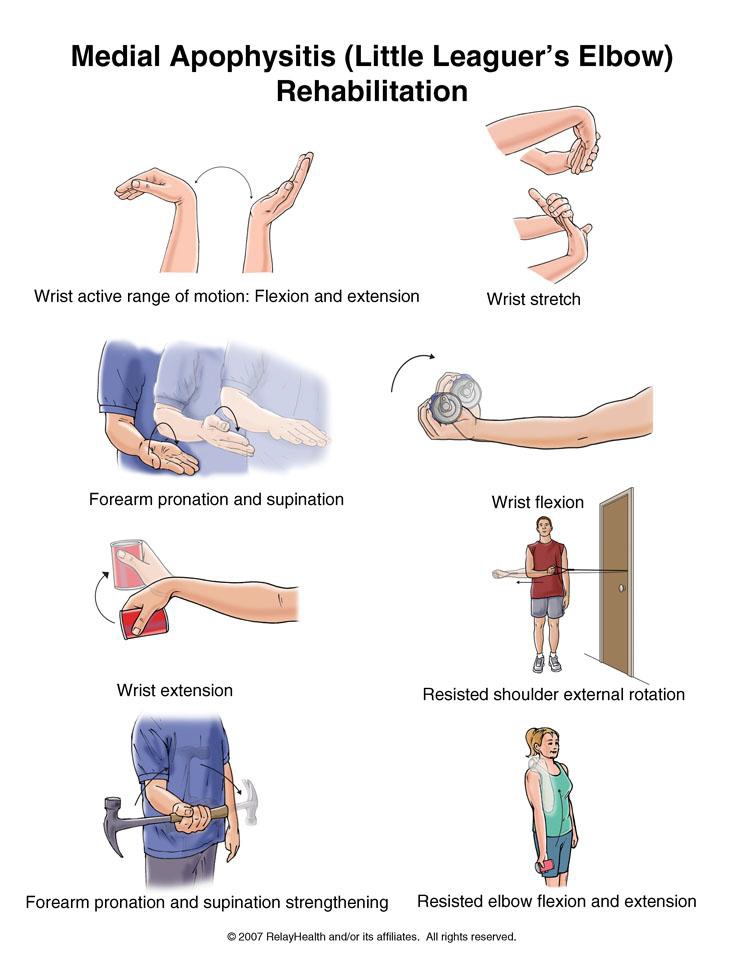
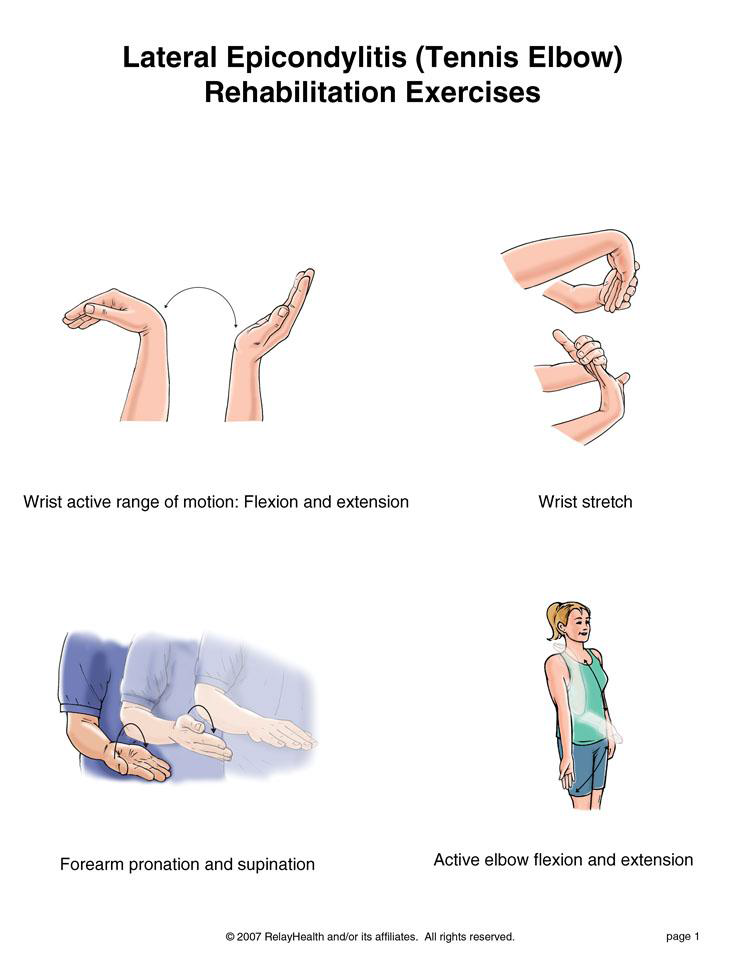
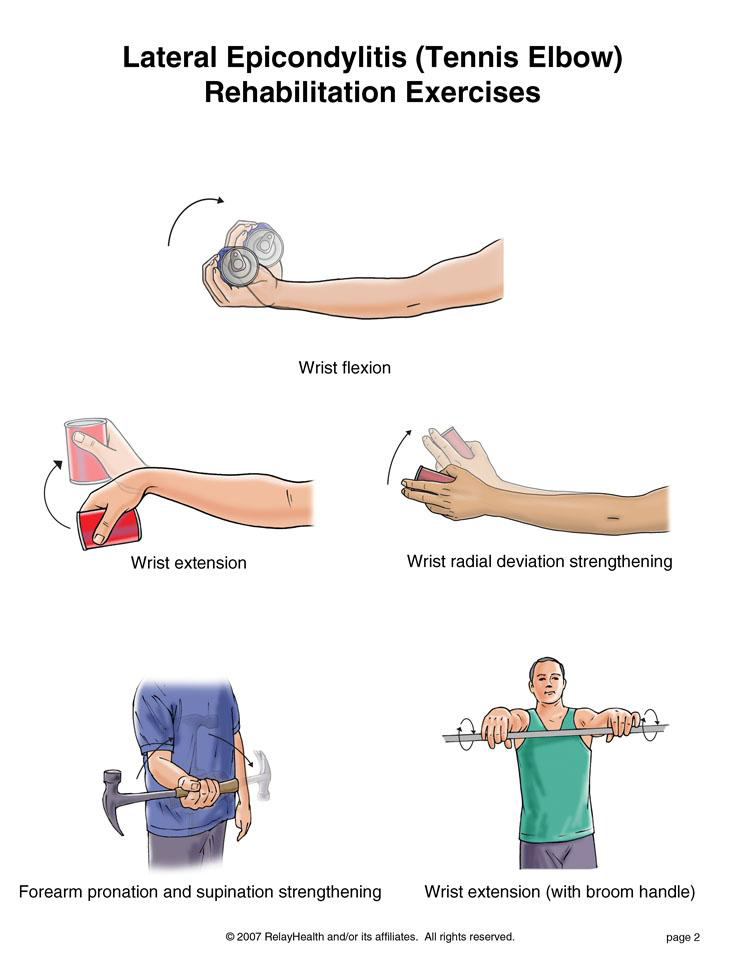
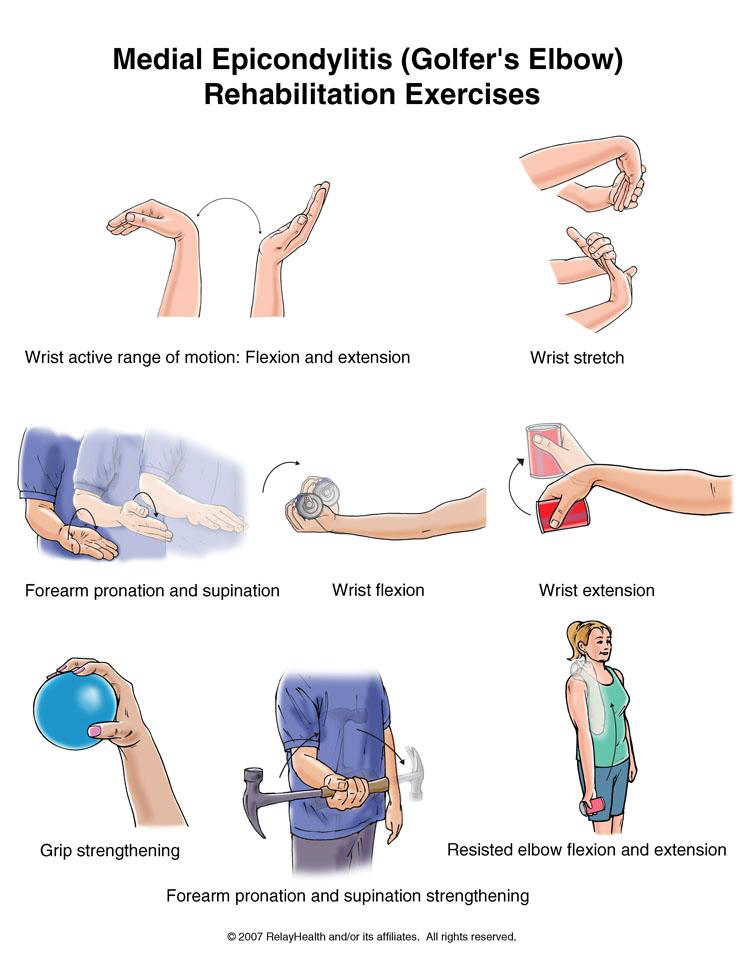
Foot Pain
Foot pain can be caused by a variety of factors, ranging from overuse injuries to underlying medical conditions. Understanding the potential causes of foot pain, when to seek medical attention, and available treatment options is essential for effective management.
Call the office or book an appointment online today.
281-256-8685
Request an Appointment
Foot Pain Q & A
What are the causes of Foot Pain?
Plantar Fasciitis: Inflammation of the plantar fascia, a thick band of tissue that runs along the bottom of the foot, often due to overuse, poor footwear, or biomechanical issues.
Achilles Tendinitis: Inflammation of the Achilles tendon, which connects the calf muscles to the heel bone, commonly caused by repetitive stress or overuse.
Metatarsalgia: Pain and inflammation in the ball of the foot, often associated with activities that involve running, jumping, or wearing high heels.
Foot Sprains: Stretching or tearing of the ligaments in the foot, typically resulting from trauma or sudden twisting movements.
Stress Fractures: Hairline cracks in the bones of the foot, commonly seen in athletes or individuals who engage in high-impact activities.
Bunions: Bony protrusions that develop at the base of the big toe, often due to genetics, improper footwear, or structural abnormalities.
Neuromas: Thickening of the tissue around a nerve in the foot, leading to pain, tingling, or numbness, commonly associated with wearing tight shoes.
Arthritis: Conditions like osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis can affect the joints of the foot, resulting in pain, stiffness, and decreased mobility.
When do you seek medical help for foot Pain?
You should seek medical attention for foot pain if:
- The pain is severe or persistent.
- You are unable to bear weight on the affected foot.
- The foot appears deformed or swollen.
- You have signs of infection, such as redness, warmth, swelling, or fever.
- The pain is accompanied by numbness or tingling in the foot.
- You have a history of foot injury or underlying medical conditions that may affect foot health.
What are treatment Options for Foot Pain?
Treatment for foot pain depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. It may include:
Rest and Immobilization: Avoiding activities that exacerbate foot pain and using supportive devices such as orthotic inserts, braces, or splints to alleviate pressure on the affected area.
Ice and Elevation: Applying ice packs to the affected foot and elevating it above heart level can help reduce swelling and alleviate pain.
Pain Management: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as acetaminophen or NSAIDs, can help alleviate pain and inflammation.
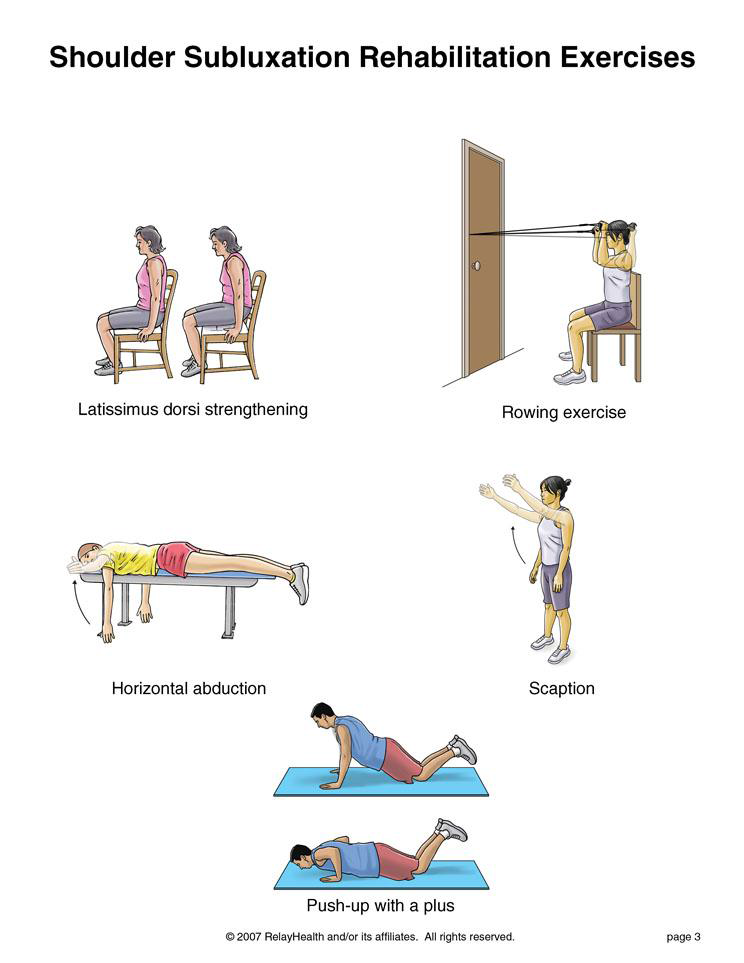
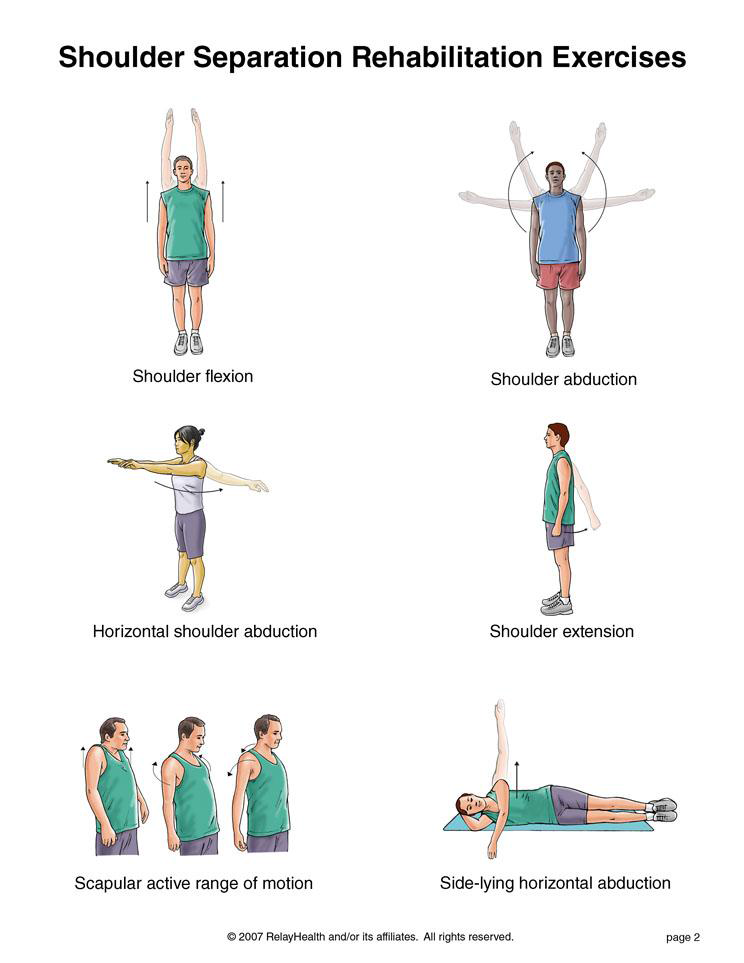
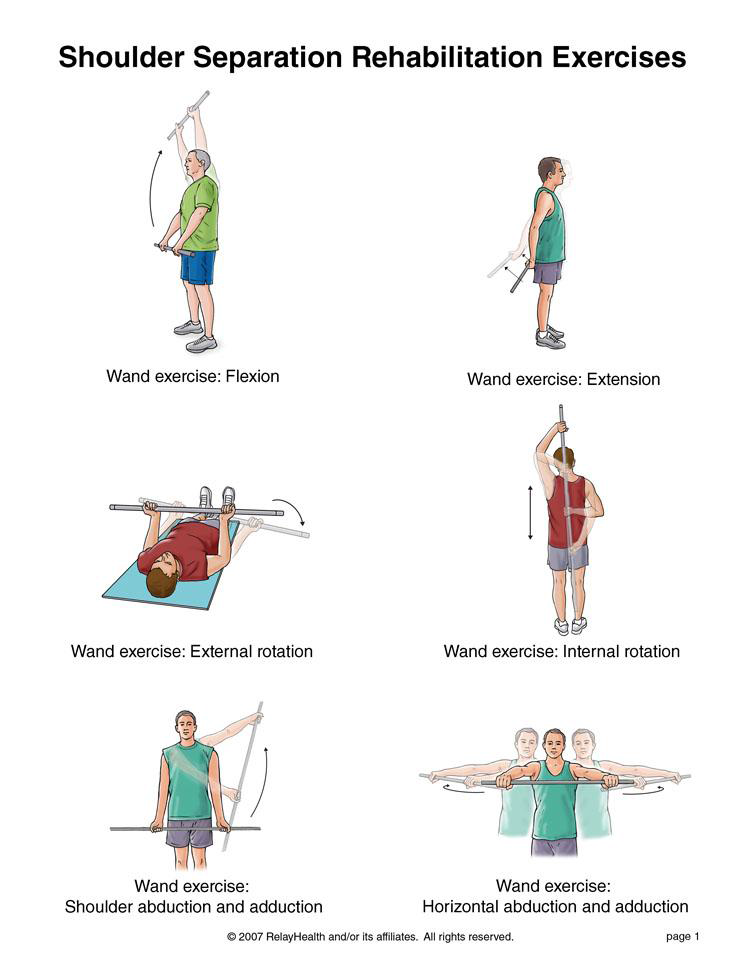
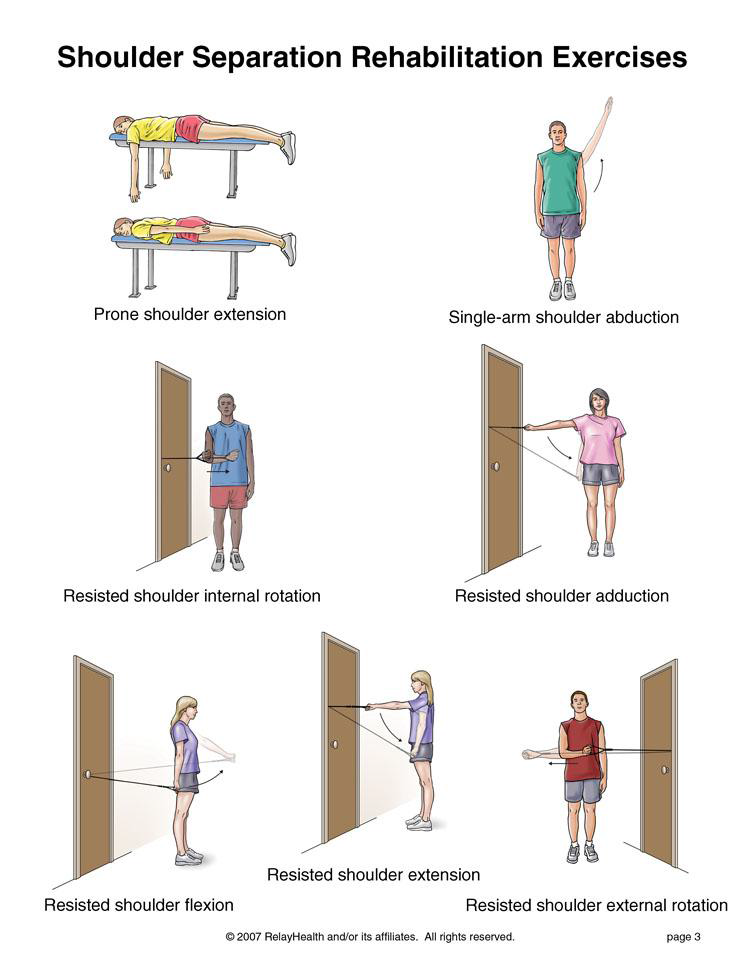
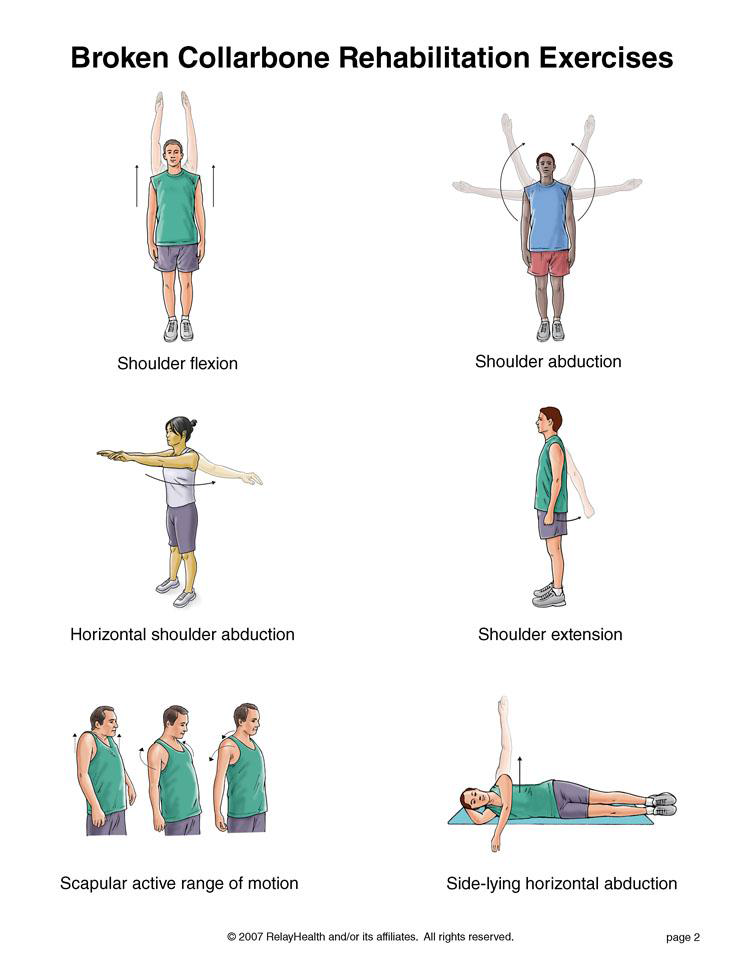
Physical Therapy: Exercises to strengthen the muscles of the foot, improve flexibility, and correct biomechanical issues contributing to foot pain.
Orthotic Devices: Custom-made shoe inserts or orthotic devices can provide support and stability to the foot and correct structural abnormalities.
Corticosteroid Injections: Injections of corticosteroids into the affected area can help reduce inflammation and relieve pain, especially for conditions like plantar fasciitis or arthritis.
Surgery: In severe cases or when conservative treatments fail, surgical interventions such as bunionectomy, tendon repair, or joint fusion may be necessary.
It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional, such as a podiatrist or orthopedic specialist, for a thorough evaluation and personalized treatment plan tailored to your specific needs. Early intervention and appropriate management can help alleviate foot pain, promote healing, and prevent further complications, allowing you to resume normal activities with minimal discomfort.
Request an Appointment
Ankle pain can stem from various causes, ranging from acute injuries to chronic conditions. Understanding the potential causes of ankle pain, when to seek medical help, and available treatment options is essential for effective management.
Call the office or book an appointment online today.
281-256-8685
Request an Appointment
Ankle Pain Q & A
What are the causes of Ankle Pain?
Causes of Ankle Sprain Include:
Sprains and Strains: One of the most common causes of ankle pain is a sprain, which occurs when the ligaments that support the ankle stretch or tear. Ankle sprains often result from twisting or rolling the ankle during physical activity. Strains involve stretching or tearing of the muscles or tendons around the ankle.
Fractures: Ankle fractures can occur when there is a break in one or more of the bones that make up the ankle joint, such as the tibia, fibula, or talus. Fractures may result from trauma, falls, or repetitive stress.
Tendonitis: Inflammation of the tendons around the ankle, such as Achilles tendonitis or peroneal tendonitis, can cause pain, swelling, and difficulty with movement. Tendonitis often develops due to overuse, repetitive strain, or sudden increases in activity.
Arthritis: Conditions like osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis can affect the joints of the ankle, leading to pain, stiffness, swelling, and decreased mobility. Arthritis may develop as a result of age-related wear and tear, autoimmune disorders, or previous injuries.
Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome: Similar to carpal tunnel syndrome in the wrist, tarsal tunnel syndrome involves compression of the posterior tibial nerve as it passes through the tarsal tunnel in the ankle. This can cause pain, tingling, numbness, or weakness in the foot and ankle.
Bursitis: Inflammation of the bursae, small fluid-filled sacs that cushion the ankle joint, can result from overuse, repetitive motion, or trauma. Bursitis can lead to pain, swelling, and tenderness around the ankle.
Stress Fractures: Tiny cracks in the bones of the ankle, known as stress fractures, can develop over time due to repetitive stress or overuse. Athletes who engage in high-impact activities like running or jumping are particularly susceptible to stress fractures.
When do you Seek Medical Help for Ankle Pain?
You should seek medical attention for ankle pain if:
- The pain is severe, persistent, or worsening over time.
- You are unable to bear weight on the affected ankle.
- The ankle appears deformed or misaligned.
- There is swelling, redness, warmth, or tenderness around the ankle joint.
- You have signs of infection, such as fever or chills.
- The pain is accompanied by numbness, tingling, or weakness in the foot or ankle.
What are the treatment Options for Ankle Pain?
Treatment for ankle pain depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. It may include:
Rest and Immobilization: Avoiding weight-bearing activities and using supportive devices like crutches, braces, or splints to stabilize the ankle and promote healing.
Ice and Elevation: Applying ice packs and elevating the affected ankle above heart level can help reduce swelling and alleviate pain.
Compression: Using compression bandages or wraps around the ankle can provide support and reduce swelling.
Physical Therapy: Exercises to strengthen the muscles around the ankle, improve flexibility, and restore range of motion.
Pain Management: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as acetaminophen or NSAIDs, can help alleviate pain and inflammation.
Corticosteroid Injections: Injections of corticosteroids into the ankle joint can help reduce inflammation and relieve pain, especially for conditions like arthritis or tendonitis.
Surgery: In severe cases or when conservative treatments fail, surgical interventions such as ankle arthroscopy, ligament repair, or ankle fusion may be necessary.
It’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional, such as an orthopedic specialist or sports medicine physician, for a thorough evaluation and personalized treatment plan tailored to your specific needs. Early intervention and appropriate management can help alleviate ankle pain, promote healing, and prevent further complications, allowing you to return to your usual activities with minimal discomfort.
Request an Appointment